 The Academy
The Academy

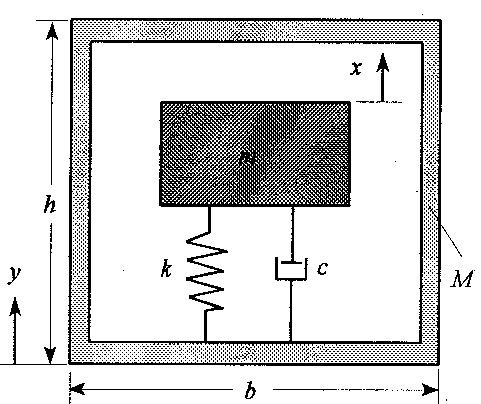
An accelerometer is an instrument that measures the acceleration of a vibrating body. Such instruments are widely used for vibration measurements in machine and structural applications. The instrument consists of a mass m, and spring k, and a damper c inside a cage, which is rigidly fastened to the vibrating body (see schematic). With such an arrangement, the bottom support of the spring and dashpot will have the same motion as the cage, y(t), while the suspended mass will undergo a different motion, x(t). The relative motion of the suspended mass with respect to the cage, z(t) = x(t) - y(t), can be calibrated and measured electronically using piezoelectric technology. The device operates under the principle that with z(t) known, the motion of the device(object) y(t) can be determined.
Recall that the basic equations governing this problem are (see text, pp 636-641)
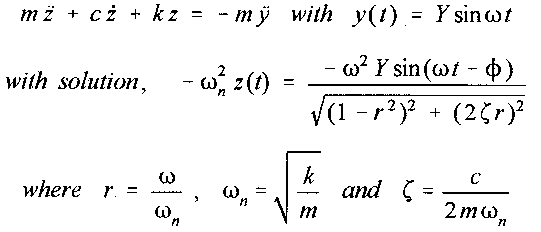
From these results we find that the acceleration of the base, |y''(t)| is given (with the exception of the phase angle) by |-wn2z(t)| if the term 1/[(1-r2)2 + 2(zeta)r)2]½ = 1. Figure 10.13 in the text illustrates the behavior of this term. If the base motion consists of a single harmonic, the phase angle will not be of importance. The problem is to design and build an accelerometer using Working Model with following constraints: